RAID 5 Data Recovery
RAID Data Recovery Services
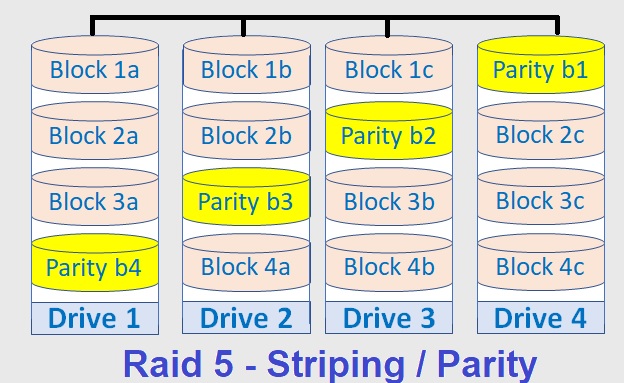
RAID 5 is the most common secure RAID level. It requires at least 3 drives but can work with up to 16. Data blocks are striped across the drives and on one drive a parity checksum of all the block data is written. The parity data are not written to a fixed drive, they are spread across all drives, as the drawing below shows.
Using the parity data, the computer can recalculate the data of one of the other data blocks, should those data no longer be available. That means a RAID 5 array can withstand a single drive failure without losing data or access to data. Although RAID 5 can be achieved in software, a hardware controller is recommended. Often extra cache memory is used on these controllers to improve the write performance.
Advantages of RAID 5
Disadvantages of RAID 5
RAID Failures
 RAID controller failure
RAID controller failure Rebuild failure
Rebuild failure Damaged striping
Damaged striping Multiple drive failure
Multiple drive failure Drive not detecting in BIOS
Drive not detecting in BIOS  Configuration damage or corruption
Configuration damage or corruption
